VAT Penalties
I have made a lot of references to penalties in other articles over the years. So I thought it would be a good idea to have a closer look; what are they, when are they levied, rights of appeal, and importantly how much could they cost if a business gets it wrong?
Overview
Broadly, a penalty is levied if the incorrect amount of VAT is declared, either by understating output tax due, or overclaiming input tax, or accepting an assessment which is known to be too low.
Amount of penalty
HMRC detail three categories of inaccuracy. These are significant, as each has its own range of penalty percentages. If an error is found to fall within a lower band, then a lower penalty rate will apply. Where the taxpayer has taken ‘reasonable care,’ even though an error has been made, then no penalty will apply.
- An error, when reasonable care not taken: 30%;
- An error which is deliberate, but not concealed: 70%;
- An error, which is deliberate and concealed: 100%.
Reasonable care
There is no definition of ‘reasonable care’. However, HMRC have said that they would not expect the same level of knowledge or expertise from a self-employed person, as from a large multi-national.
HMRC expect that, where an issue is unclear, advice is sought, and a record maintained of that advice. They also expect that, where an error is made, it is adjusted, and HMRC notified promptly. They have specifically stated that merely to adjust a return will not constitute a full disclosure of an error. Therefore, a penalty may still be applicable.
Notification
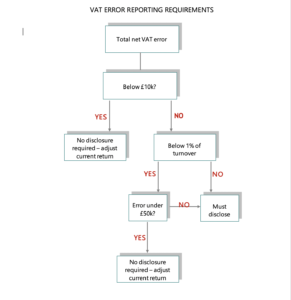
What the penalty is based on
The amount of the penalty is calculated by applying the appropriate penalty rate (above) to the ‘Potential Lost Revenue’ or PLR. This is essentially the additional amount of VAT due or payable, as a result of the inaccuracy, or the failure to notify an under-assessment. Special rules apply where there are a number of errors, and they fall into different penalty bands.
Defending a penalty
The percentage penalty may be reduced by a range of ‘defences:’
– Telling; this includes admitting the document was inaccurate, or that there was an under-assessment, disclosing the inaccuracy in full, and explaining how and why the inaccuracies arose;
– Helping; this includes giving reasonable help in quantifying the inaccuracy, giving positive assistance rather than passive acceptance, actively engaging in work required to quantify the inaccuracy, and volunteering any relevant information;
– Giving Access; this includes providing documents, granting requests for information, allowing access to records and other documents.
Further, where there is an ‘unprompted disclosure’ of the error, HMRC have power to reduce the penalty further. This measure is designed to encourage businesses to review their own VAT returns.
A disclosure is unprompted if it is made at a time when a person had no reason to believe that HMRC have discovered or are about to discover the inaccuracy. The disclosure will be treated as unprompted even if at the time it is made, the full extent of the error is not known, as long as fuller details are provided within a reasonable time.
HMRC have included a provision whereby a penalty can be suspended for up to two years. This will occur for a careless inaccuracy, not a deliberate inaccuracy. HMRC will consider suspension of a penalty where, given the imposition of certain conditions, the business will improve its accuracy. The aim is to improve future compliance and encourage businesses which genuinely seek to fulfil their obligations.
Appealing a penalty
HMRC have an internal reconsideration procedure, where a business should apply to in the first instance. If the outcome is not satisfactory, the business can pursue an appeal to the First Tier Tribunal. A business can appeal on the grounds of; whether a penalty is applicable, the amount of the penalty, a decision not to suspend a penalty, and the conditions for suspension.
The normal time limit for penalties to four years. Additionally, where there is deliberate action to evade VAT, a 20 year limit applies. In particular, this applies to a loss of VAT which arises as a result of a deliberate inaccuracy in a document submitted by that person.
These are just the penalties for making “errors” on VAT returns. HMRC have plenty more for anything from late registration to issuing the wrong paperwork.
Even darker
There are even more severe penalties for deliberate acts, including significant terms of imprisonment. That is the subject of another article.
Assistance
My advice is always to check on all aspects of a penalty and seek assistance for grounds to challenge a decision to levy a penalty. We have a very high success rate in defending businesses against inappropriate penalties. It is always worth running a penalty past us.
