Where detailed records are unavailable it does not mean there is a lower standard of proof for a claim. The civil standard of proof (on a balance of probabilities) remains.
Where detailed records are unavailable it does not mean there is a lower standard of proof for a claim. The civil standard of proof (on a balance of probabilities) remains.
HMRC has published updated guidance on deliberate behaviour. It clarifies the definition of these actions in respect of extended time limits.
What is deliberate behaviour?
A deliberate inaccuracy in a document occurs when a person (or another person acting on behalf of that person) knowingly gives HMRC an inaccurate document.
“A person who submits a document containing a deliberate inaccuracy might assert that they did not intend to cause a loss of tax. For the purpose of assessing this loss of tax, the person or any persons acting on their behalf will be treated as deliberately causing the loss of tax if they consciously intended to mislead HMRC”.
Examples
(This list is not exhaustive and HMRC provide more examples in the guidance).
Why is it important?
Mainly, there are different time limits within which HMRC can take action.
A 20 year time limit applies where tax has been underdeclared, or over-repaid, as a result of a deliberately inaccurate return or other document. The normal cap is four years.
Other action
Although HMRC can make assessments to recover any tax lost, it also have a criminal investigation policy and will refer the most serious cases for consideration of criminal proceedings where appropriate.
If you or your clients are subject to an investigation, please seek professional advice immediately. There is a dark side to VAT.
Further to my article on repayment interest, I thought it may be helpful if I looked at how HMRC process repayment returns, and what can delay payments.
Once a business submits a repayment return it is subject to a number of set steps:
HMRC records the date a return is submitted online via MTD.
Automated credibility checks are applied to all claims. HMRC say that most returns pass these tests. If this is the case, they proceed immediately for payment.
Credibility queries (or “pre-cred” queries) – returns that fail the automated tests are checked manually and are either resolved by the credibility team, or sent to officers to carry out further investigation.
Returns sent for further checks – HMRC say that high priority is given to these verifications and any queries are handled with the minimum involvement of, or inconvenience to, a business. Experience insists that this is not always the case.
Credibility queries are returned to the credibility team – results of the officer’s action, including any amendments required, are returned with a certificate detailing the amount of time taken and any official delay. Claims are passed for payment.
Payment of the claim – once a claim has been accepted, repayment is made immediately. HMRC’s systems check whether repayment interest is applicable. If it is, the interest is paid automatically at the same time as the repayment.
Commentary
Most issues usually arise when returns show “unexpected” repayments – eg; a business regularly submitting payment returns submits an one-off claim, or when a first return shows a significant repayment. The pre-cred checks are undertaken to protect the revenue, that is; to ensure that the claim is valid before money is released. Normally, these checks involve a request for copies of purchase invoices, a telephone conversation, or a physical visit by an officer. Not unreasonably, the quantum of the claim impacts significantly the way HMRC handle it.
However, delays can occur on both sides. A business will have to reply to all HMRC requests timeously (and this is in its interest) but more often a claim will be ‘lost” in the system, or inspectors take an unacceptable time to deal with queries. I have one claim that is still in the system after being lodged in January 2021, despite us providing all information requested immediately.
Reasons for unexpected repayments
There are a number of reasons why a return may be an unusual repayment, which include, but are not limited to a:
HMRC has published new guidance on repayment interest – in cases where HMRC is late in settling a repayment claim for overpaid VAT.
If HMRC is late in paying an amount representing a repayment, ie; when a return shows more input tax than output tax, or a claim is made for VAT previously overpaid, a business may be entitled to repayment interest on the VAT that it is owed. From 1 January 2023 repayment interest replaced the repayment supplement.
Amount of interest
Repayment interest is paid at the Bank of England base rate minus 1%, with a minimum rate of 0.5%.
Start date
VAT already paid to HMRC
The day after the later of these two dates:
VAT not paid to HMRC
The day after the later of these two dates:
End date
Repayment interest ends when HMRC either repays the VAT or sets it off against a different VAT or tax amount that is deemed to be owed.
Notes
Latest from the courts
In the First-Tier Tribunal (FTT) case of The Squa.re Limited (TSL) the issue was whether unsold inventory or inventory sold at a loss could affect the calculation of the Tour Operators’ Margin Scheme (TOMS).
Background
TSL provided serviced apartments to travellers. The company leased accommodation from the owners of the properties who were frequently, if not exclusively, private individuals who were not registered for VAT.
These leases were often for an extended period, eg; annual leases, such that the appellant is committed under the terms of the lease even where the accommodation cannot then be on supplied or not supplied for a profit.
The Issue
The issue was whether TOMS operated in such a way as to permit a negative calculation resulting in repayment to the appellant. HMRC issued an assessment because, while they accepted that there may be a zero margin on a TOMS supply, they considered that a negative margin was not permitted by the scheme. TSL maintained that a repayment of overdeclared output tax was appropriate if a loss was made (an “overall negative margin”) as TOMS does not exclude the possibility of a negative margin.
The dispute between the parties was a technical one only and concerned the interpretation of the statutory provisions implementing TOMS into UK law.
Legal
The domestic implementation of the TOMS is authorised by The Value Added Tax Act 1994, Section 53 and found in Value Added Tax (Tour Operators’) Order 1987 (SI1987/1806). Guidance is provided via Notice 709/5 and Sections 8 to 13 have the force of law.
Decision
The Tribunal determined that it was clear from the legislation that the taxable amount is concerned with the supply made, and not the VAT incurred on the various cost components. Under normal VAT accounting the output tax charged on supplies is calculated by reference to the consideration received by the supplier from the customer. There can realistically be no concept of negative consideration.
The FTT considered that there is no basis inherent within TOMS which would permit a calculation of a negative sum. There had been a supply (of a designated travel service) for a consideration, and it is the taxable amount of that supply which was to be determined. A negative taxable amount is a “conceptual impossibility”. A negative margin arises as a consequence of a lack of profitability, but VAT is a transaction tax and not a tax on profit.
When sold at a loss where the total calculation resulted in a negative margin the annual sum due by way of output tax would be nil (not a repayment).
Where the accommodation is not sold at all, the FTT noted that this cost represented a cost of doing business but, on the basis that there has been no onward supply, there is no supply which meets the definition of a designated travel service. The relevant accommodation is not for the direct benefit of any traveller so there is no supply and TOMS is irrelevant.
Whilst the FTT considered that were it the case that identified costs incurred in buying in goods and services which are not then the subject of an onward supply should be excluded from TOMS calculations, costs associated with the block booking of accommodation of the type incurred by TSL were to be included. Where such costs exceed the value obtained by onward supply, the negative margin forms part of the annual calculation. However, where the global calculation results in a negative margin the tax due for the year under TOMS is nil and there was no basis for a repayment to TSL.
There was no basis on which to permit an overall TOMS negative margin and the appeal was dismissed.
Commentary
Another demonstration of the complexities of TOMS and the potential pitfalls.
It may be useful to note that input tax claims are not permitted in TOMS calculations, however, any VAT incurred on any bought in, but unsold, services would not be excluded from recovery as there is no TOMS supply. The input tax on unsold inventory was a general cost of doing business and, as such, recoverable in the normal way. Consequently, there may be circumstances for businesses using TOMS where input tax incurred on unsold elements may be claimed outside of TOMS
I am often asked what the most frequent VAT errors made by a business are. I usually reply along the lines of “a general poor understanding of VAT, considering the tax too late or just plain missing a VAT issue”. While this is unquestionably true, a little further thought results in this top ten list of VAT horrors:
So, you may ask: “How do I make sure that I avoid these VAT pitfalls?” – And you would be right to ask.
Of course, I would recommend that you engage a VAT specialist to help reduce the exposure to VAT costs!
Further to my article on the Domestic Reverse Charge (DRC) for builders being deferred, HMRC has announced a further delay from 1 October 2020 until 1 March 2021 due to the impact of the coronavirus on the construction sector.
Revenue and Customs Brief 7 (2020 sets out the details.
Changes
HMRC announced that there will be an amendment to the original legislation, which was laid in April 2019, to make it a requirement that for businesses to be excluded from the reverse charge because they are end users or intermediary suppliers, they must inform their sub-contractors in writing that they are end users or intermediary suppliers. Details of the DRC here and here.
Latest from the courts
In the recent First Tier Tribunal (FTT) case of Aitmatov Academy an otherwise unremarkable case illustrates the care required when making input tax claims.
The quantum of the claim was low and the technical issues not particularly complex, however, it underlined some basic rules for making a VAT claim.
Background
A doctor organised a cultural event at the House of Lords for which no charge was made to attendees. The event organiser as shown on the event form was the doctor. Aitmatov Academy was shown as an organisation associated with the event. It was agreed that the attendees were not potential customers of Aitmatov Academy and that the overall purpose of the event was cultural and not advertising.
Issues
HMRC disallowed the claim. The issues were:
Decision
The FTT found that the Academy incurred the cost and consequently must have concluded that the Academy was the recipient of the supply, not the doctor.
However, the judge decided that the awards ceremony was not directly or indirectly linked to taxable supplies made or intended to be made by the Academy, and therefore that the referable input tax should not be allowed. Consequently, the court did not need to consider whether the event qualified as business entertainment.
On a separate point, the appellant contended that, as a similar claim had been paid by HMRC previously, she could not see the difference that caused input VAT in this case to be disallowed. The Tribunal explained that its role is to apply the law in this specific instance and as such it cannot look at what happened in an early case which is not the subject of an appeal.
Commentary
A helpful reminder of some of the tests that need to be passed in order for an input tax claim to be valid. I have written about some common issues with claims and provided a checklist. Broadly, in addition to the tests in this case, a business needs to consider:
I have also looked at which input tax is specifically barred.
Finally, “entertainment” is a topic all of its own. I have considered what is claimable here in article which includes a useful flowchart.
As always, the message is; if a business is to avoid penalties and interest, if there is any doubt over the validity of a claim, seek advice!
VAT Penalties
I have made a lot of references to penalties in other articles over the years. So I thought it would be a good idea to have a closer look; what are they, when are they levied, rights of appeal, and importantly how much could they cost if a business gets it wrong?
Overview
Broadly, a penalty is levied if the incorrect amount of VAT is declared, either by understating output tax due, or overclaiming input tax, or accepting an assessment which is known to be too low.
Amount of penalty
HMRC detail three categories of inaccuracy. These are significant, as each has its own range of penalty percentages. If an error is found to fall within a lower band, then a lower penalty rate will apply. Where the taxpayer has taken ‘reasonable care,’ even though an error has been made, then no penalty will apply.
Reasonable care
There is no definition of ‘reasonable care’. However, HMRC have said that they would not expect the same level of knowledge or expertise from a self-employed person, as from a large multi-national.
HMRC expect that, where an issue is unclear, advice is sought, and a record maintained of that advice. They also expect that, where an error is made, it is adjusted, and HMRC notified promptly. They have specifically stated that merely to adjust a return will not constitute a full disclosure of an error. Therefore, a penalty may still be applicable.
Notification
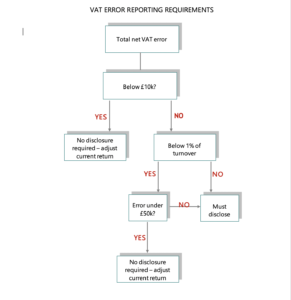
What the penalty is based on
The amount of the penalty is calculated by applying the appropriate penalty rate (above) to the ‘Potential Lost Revenue’ or PLR. This is essentially the additional amount of VAT due or payable, as a result of the inaccuracy, or the failure to notify an under-assessment. Special rules apply where there are a number of errors, and they fall into different penalty bands.
Defending a penalty
The percentage penalty may be reduced by a range of ‘defences:’
– Telling; this includes admitting the document was inaccurate, or that there was an under-assessment, disclosing the inaccuracy in full, and explaining how and why the inaccuracies arose;
– Helping; this includes giving reasonable help in quantifying the inaccuracy, giving positive assistance rather than passive acceptance, actively engaging in work required to quantify the inaccuracy, and volunteering any relevant information;
– Giving Access; this includes providing documents, granting requests for information, allowing access to records and other documents.
Further, where there is an ‘unprompted disclosure’ of the error, HMRC have power to reduce the penalty further. This measure is designed to encourage businesses to review their own VAT returns.
A disclosure is unprompted if it is made at a time when a person had no reason to believe that HMRC have discovered or are about to discover the inaccuracy. The disclosure will be treated as unprompted even if at the time it is made, the full extent of the error is not known, as long as fuller details are provided within a reasonable time.
HMRC have included a provision whereby a penalty can be suspended for up to two years. This will occur for a careless inaccuracy, not a deliberate inaccuracy. HMRC will consider suspension of a penalty where, given the imposition of certain conditions, the business will improve its accuracy. The aim is to improve future compliance and encourage businesses which genuinely seek to fulfil their obligations.
Appealing a penalty
HMRC have an internal reconsideration procedure, where a business should apply to in the first instance. If the outcome is not satisfactory, the business can pursue an appeal to the First Tier Tribunal. A business can appeal on the grounds of; whether a penalty is applicable, the amount of the penalty, a decision not to suspend a penalty, and the conditions for suspension.
The normal time limit for penalties to four years. Additionally, where there is deliberate action to evade VAT, a 20 year limit applies. In particular, this applies to a loss of VAT which arises as a result of a deliberate inaccuracy in a document submitted by that person.
These are just the penalties for making “errors” on VAT returns. HMRC have plenty more for anything from late registration to issuing the wrong paperwork.
Even darker
There are even more severe penalties for deliberate acts, including significant terms of imprisonment. That is the subject of another article.
Assistance
My advice is always to check on all aspects of a penalty and seek assistance for grounds to challenge a decision to levy a penalty. We have a very high success rate in defending businesses against inappropriate penalties. It is always worth running a penalty past us.
COVID-19 Update
HMRC has published concessions in VEXP30310 relating to the conditions for the zero rating of exports.
Background
Most exports of goods from the UK are subject to zero rating. However, in order for VAT free treatment to apply, certain conditions must be met, otherwise 20% VAT applies to the sale. One of the conditions is that the goods must be exported within specified time limits.
Time limits
Generally, goods can be zero rated provided that:
COVID-19
During the pandemic, it may not be possible for businesses to export goods within the prescribed time. HMRC recognises that some intended exports have been delayed due to circumstances outside a business’ control. Therefore, the guidance sets out the circumstances in which HMRC may agree to additional time for the export before any tax is collected.
Additional time
The time limits for the export of goods from the UK are set out in legislation. However, HMRC has discretion to permit non-observance of the conditions and time limits for export of goods – VAT Act 1994, Section 30(10). HMRC has said that it will use its discretion to temporarily waive the prescribed time limits for export on a case by case basis. The goods must, however, have either already been exported or will be as soon as is reasonably practicable after the date a business is notified that HMRC is temporarily waiving the tax. An application for HMRC to waive the time limits must be made in writing.
Conditions
HMRC will permit a temporary waiver of time limits if the following conditions are met:
Examples include:
This list is not exhaustive.
2. the goods have been/will be exported or removed at the earliest opportunity
3. all other conditions for zero rating exports or removals are met – exporters’ responsibilities here
Expiry
Any waiver will expire
whichever is the earlier.
If a business considers there are extenuating circumstances that mean additional time is needed to export goods beyond that permitted by the extension, it should contact HMRC setting out the details in full.
Evidence
A business must retain evidence that supports its case for the waiver (eg; cancellation notes demonstrating that the transport intended to use to take goods out of the UK did not take place, or screen shots of government rules preventing the export or removal of the goods).
Please contact us if you require any further advice or assistance.